Now there have appeared a lot of public places with dense pedestrian flow in the large-and-medium-sized cities around the world, such as subway stations, railway stations, airports, theaters, gyms, stadiums and shopping malls. The dense pedestrian flow frequently appears in these places during the rush hour and tourism season, which results in the problems in city management and planning, public security warning and smart business decision, such as security, traffic dispersion, estimate of pedestrian flow and preference analysis. In urgent need is the smart analysis of pedestrian flow which serves the estimate of pedestrians, measurement of pedestrian density, recognition of individuals and trajectory tracking.
Cooperating with University of Technology Sydney, Beijing Jiaotong University and other partners, the internet of things research team of the College of Computer Science of IMU proposes to solve the problem of the analysis of pedestrian flow with the technology of WiFi sniffing and has made the significant research achievements. The team publishes its achievements named “Pedestrian Flow Estimation Through Passive WiFi Sensing” in the 4th Issue of Volume 20 of IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing(page 1529 to 1542; its download website: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8936381), a top international journal in the field of wireless internet and mobile computing. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing is a Class A journal ranked by China Computer Federation and also a top journal listed in the Class A Category of SCI journal partition table of Chinese Academy of Sciences and its impact factor is 5.112.
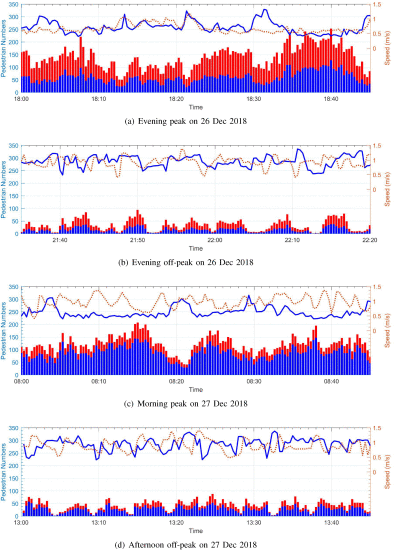
The article reveals the interactions between WiFi-sniffing results and characteristics of moving pedestrians flow and establishes the WiFi-sniffing-based theoretical model for sensing moving pedestrian flow. On that basis a sequential filtering algorithm is proposed based on the Rao-Blackwellized particle filter to produce simultaneous and efficient estimates of the pedestrian flow speed and pedestrian number by utilizing the real-time sniffing results(As is shown by the pictures above). In order to validate this study, an experimental pedestrian surveillance system using WiFi sniffers is deployed at the transfer channel of a metro station in Guangzhou, China(As is shown by the pictures below). Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed algorithm.

Huang Baoqi, is professor of the College of Computer Science of IMU, PhD candidate supervisor and the first author and corresponding author of the article. Inner Mongolia University is the institution which the first author is with. This research is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 41871363 and 61461037), Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China (Grant No. 2017JQ09), “Grassland Elite” Project of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Grant No. CYYC5016) and Chinese Scholarship Council.

