Recently, Li Zhe, associate research fellow with the Department of Mongolian History of IMU, published, as the sole author, the latest research result in international top archaeological journal- Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports (A&HCI-included). The article is titled “New opportunities for archaeological research in the Greater Ghingan Range, China: Application of UAV LiDAR in the archaeological survey of the Shenshan Mountain”(URL of the article: https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1hc6c,rVDBflgv).

Fig. 1 First page of the article
LiDAR can penetrate the vegetation to detect the ancient ruins under it. In the past 10 years it has played a key role in the archaeological research in Central America(Maya ruins) and in Southeast Asia(Angkor Wat ruins), led to many significant achievements and is widely used in the archaeological research in Europe and America. However, the application of LiDAR in the archaeological research in China is seldom reported.
With the application of UAV LiDAR and photogrammetry, the research carried out the archaeological survey of Shenshan Mountain, which sits southeast of Greater Ghingan Range, China. Through the point cloud classification of the archaeological targets(Fig.2), the research successfully filter the influence of the aboveground vegetation(Fig. 3A and Fig4.A) and in combination with the field survey, finally revealed the extent and complexity of the archaeological structures under the forest as well as their topographical context (Fig. 3B) to deliver a holistic picture of the archaeological sites in that area. After the collection of relics and analysis of archaeological sites, it is tentatively determined that Shenshan Mountain ruins are one of the sacrifice ruins in Liao Dynasty. According to this, the article further analyzes the archaeological detectability of LiDAR in areas covered by the similar vegetation, discusses the great potential of LiDAR for monitoring of grave-looting and heritage protection and emphasizes the significance of field survey for remote-sensing archaeological research and archaeological survey and analysis from the perspective of landscape archeological research.
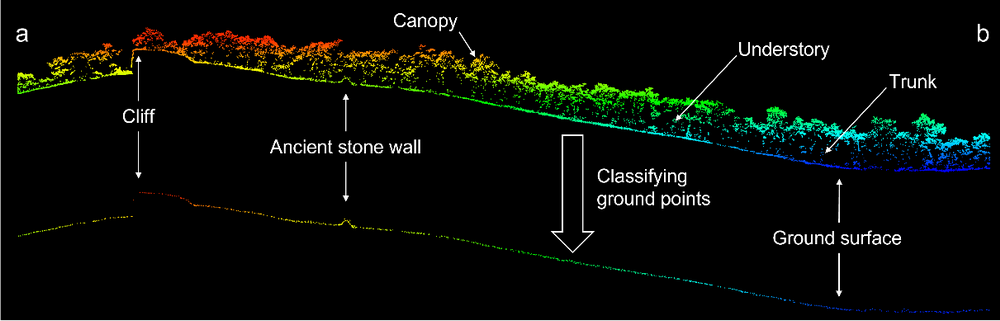
Fig.2 The point cloud classification of archaeological targets
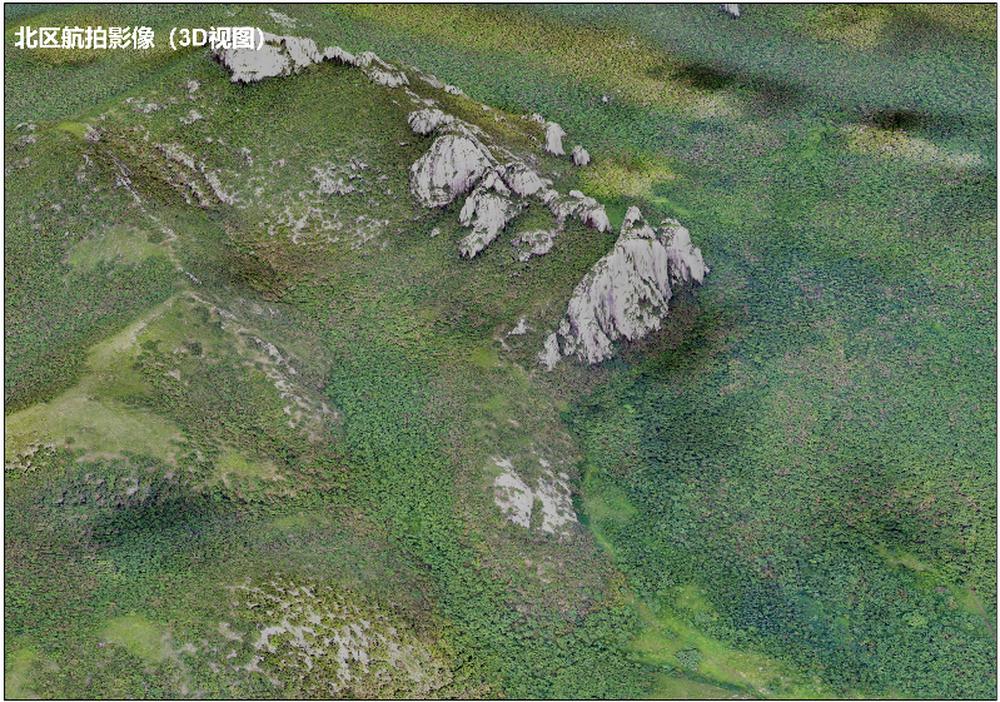

Fig. 3(A) Ariel photo of north area in which dense vegetation covers ground ancient relics and terrain.
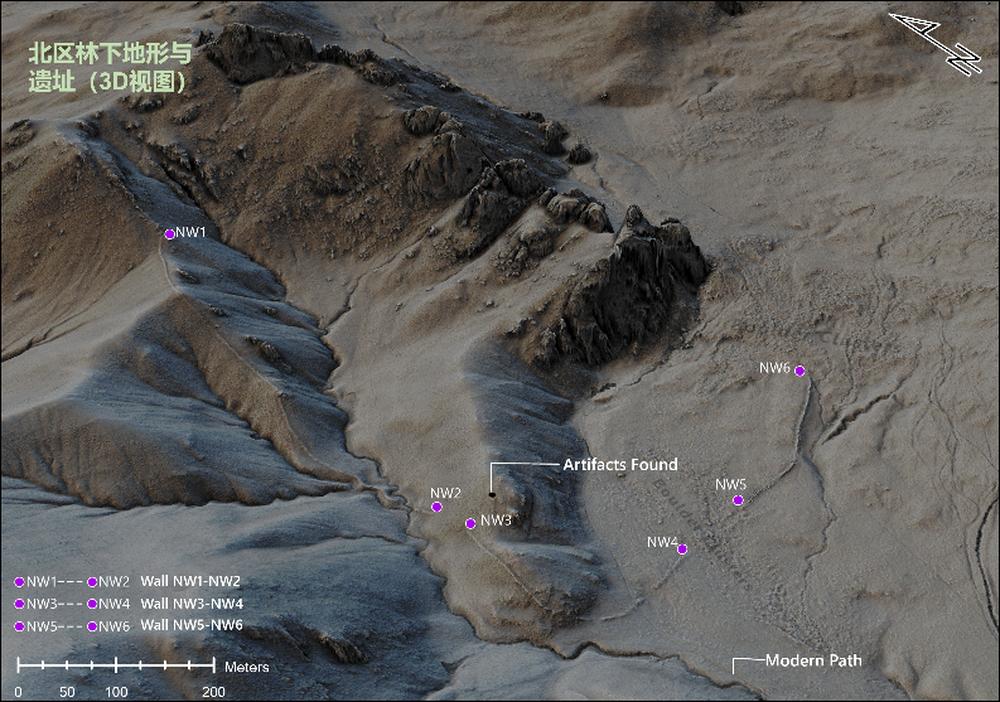
Fig. 3(B) Digital elevation map of LiDAR in which detailed terrain and ancient relics(stone walls) are clearly detected.
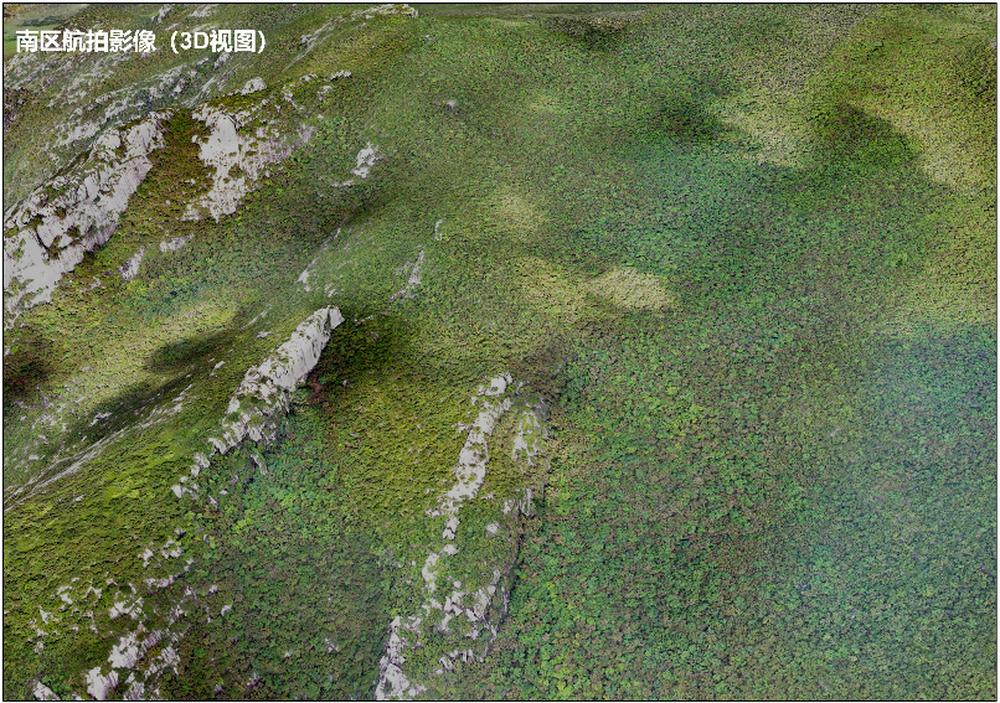

Fig. 4(A) Ariel photo of south area in which dense vegetation covers ground ancient relics and terrain.
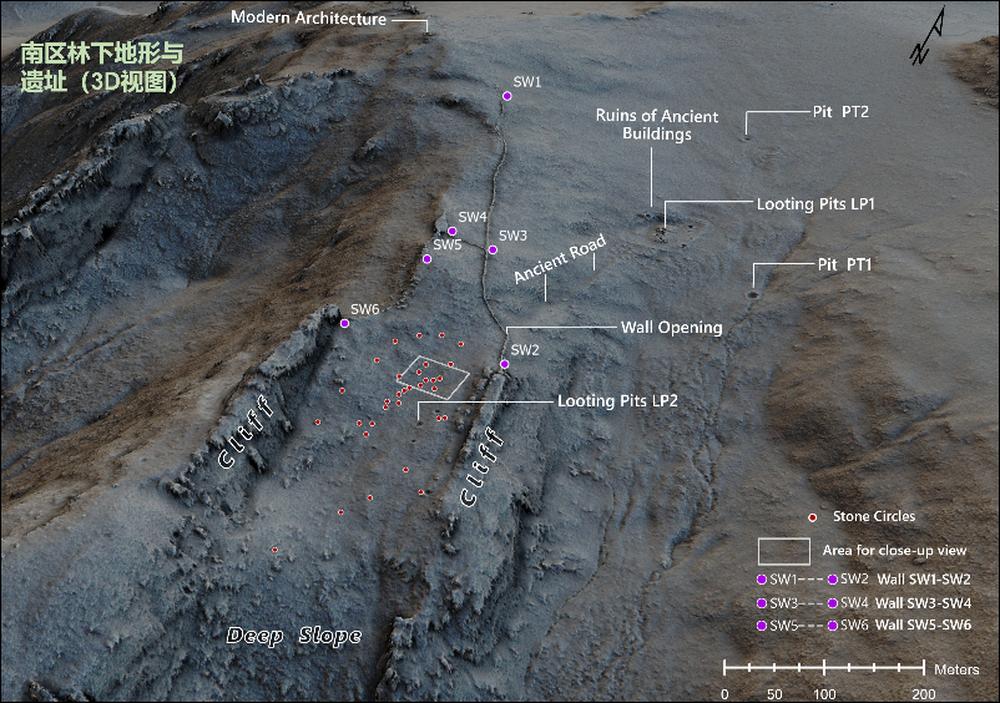
Fig. 4(B) Elevation map of LiDAR in which detailed terrain and ancient relics(sections of stone walls, ruins of ancient buildings, ancient road, stone circles, wall breach, holes and looting pit) are clearly detected.
On the one hand, the research provides the most comprehensive basic data for the further study of Shenshan ruins; and on the other hand it verifies the effectiveness of LiDAR in the area, further extends the areas where LiDAR is used in archaeological research around the world, supplies new approaches and new opportunities for the archaeological research and cultural heritage protection in Great Ghingan Range and areas covered by similar vegetation and offers a case reference for remote sensing archaeological research in forest areas in China.
Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports mainly publishes high-quality articles concerning the application of natural science and technologies and approaches in archaeology. The journal is academically influential in the world and has been selected as one of the journals listed in the first section of JCR by A&HCI.