Recently,the joint research team of Prof. Wu Limin with the College of Energy Materials and Chemistry of IMU and Prof. Gu Xiaojun with the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering has made important progress in its research. The research result concerned has been published in the international top chemistry journal- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.. The title of the research result is “Carbon Nitride Pillared Vanadate Via Chemical Pre-Intercalation Towards High-Performance Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries”(URL of the article:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202303529). And the article has been selected as Hot Paper. Xu Yue, PhD student of the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering who was admitted to IMU in 2020, is the first author of the article. Prof. Wu Limin, Prof. Gu Xiaojun, Associate Prof. Guo Yan and Prof. Yu Le with Beijing University of Chemical Technology are the co-corresponding authors of the article. IMU is the institution the first author of the article is with.

As an advanced energy storage system, aqueous zinc-ion batteries are quite safe, of low cost and widely watched. Vanadium-based oxides with tunable layered structure and high theoretical capacity are considered as one of promising cathode materials for AZIBs. Unfortunately, vanadium-based cathode is facing such challenges as narrow interlayer spacing, low intrinsic conductivity and vanadium dissolution, which largely limit its reversible capacity and cycling performance. Due to this, this research develops the strategy of chemical pre-intercalation to design carbon nitride (C3N4) pillared ammonium vanadate (NH4V4O10, denoted as NVO) nanobelts with enlarged interlayer spacing and abundant oxygen vacancies(Figure 1) as the cathode material for high-performance aqueous zinc (Zn)-ion batteries (AZIBs). In the research, the researchers also systematically studied the micro-structure of the material and the assembled batteries’ performance and regime to store energy.
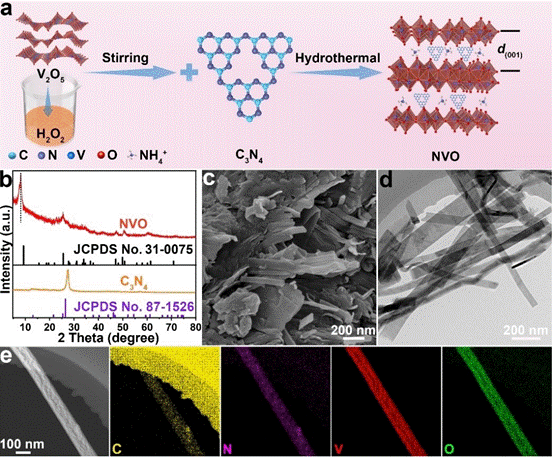
Figure 1 Synthesis of NVO nanobelts and their structural characterization
During the synthesis of the material, C3N4 nanosheets, as the nitrogen source, can be etched by H2O2 solution to release NH4+ ions and transform the V2O5 into layered NVO. More importantly, the C3N4 nanosheets formed during the etching could in situ intercalate into the layered structure to expand the interlayer spacing. Owing to the pillared structure and abundant oxygen vacancies formed by C3N4 intercalation, the conductivity and charge and ion transfer kinetics in the NVO cathode are promoted. The obtained NVO cathode delivers an exceptional rate capability of 194.7 m Ah g−1 at 20 A g−1 and ultra-long cycling life over 10,000 cycles at 10 A g−1 and demonstrates a remarkable cycling stability and high reversibility(Figure 2). In addition, the calculations results based on the density functional theory demonstrate that NVO can better combine with zinc to accelerate the charge transfer at the interface of electrodes/electrolyte.
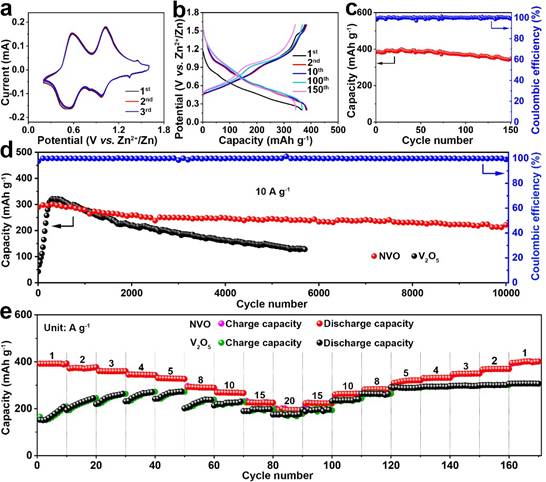
Figure 2 Performance of NVO-nanobelts-based zinc-ion batteries
In summary, the research provides a new path for designing vanadium-based cathode materials with new structure and a new strategy for highly enhancing the rate capability and cycling life of aqueous zinc-ion batteries. The research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science and Technology Projects of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region and the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia.

